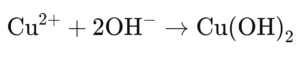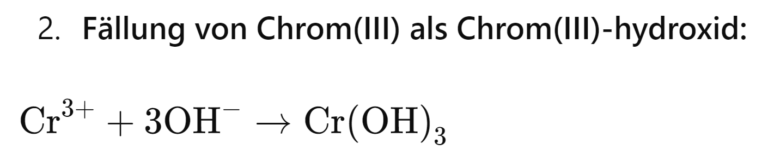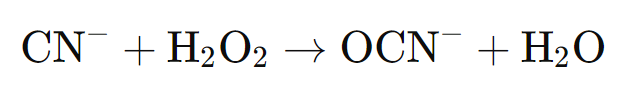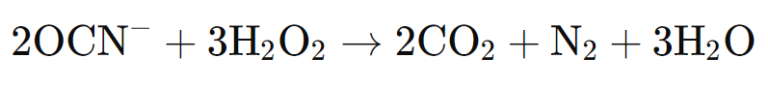Physico-chemical treatment of industrial wastewater is an essential process for regulatory compliance and environmental protection. In this article, we will explain the basics of physico-chemical treatment of wastewater, including cyanide detoxification, heavy metal precipitation, chromium (VI) reduction and pre-treatment for water recycling.
Table of contents
Basics of chemical-physical wastewater treatment
Industrial chemical-physical wastewater plants (CP plants) are designed to treat the wastewater generated in the production process in order to meet the regulatory requirements for discharge into bodies of water or municipal wastewater treatment plants. This treatment often takes place in several stages in order to effectively remove various contaminants such as heavy metals, COD, lipophilic substances or AOX.
Precipitation and flocculation are central processes in chemical-physical wastewater treatment that aim to convert dissolved and suspended substances into insoluble or larger particles that can then be removed from the water.

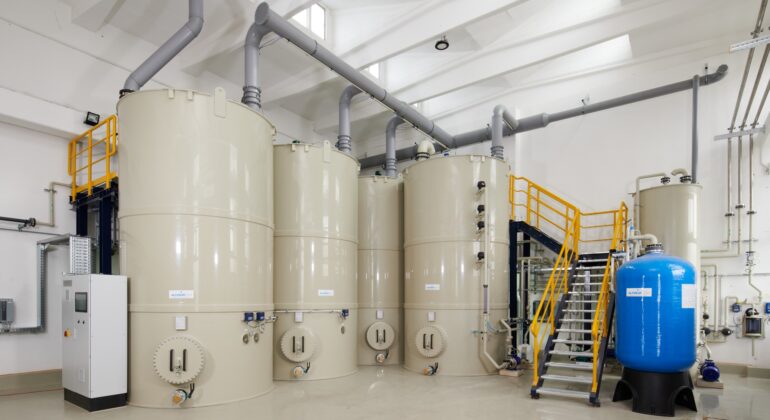
Photo: CP system as a batch system for the removal of heavy metals, AOX and cyanide (system: ALMA CHEM MCW)
The felling process
Precipitation is a process in which dissolved substances, in particular heavy metals, are converted into an insoluble form through chemical reactions. This is achieved by adding precipitants based on metal salts and adjusting the pH value so that the substances to be precipitated have the lowest water solubility (neutralization precipitation).
Precipitation process:
- Addition of precipitants: A defined quantity of precipitants such as iron(III) chloride or polyaluminum chloride is added to the wastewater.
- pH value adjustment: The pH value is adjusted to the optimum range in which the pollutants are least soluble by adding neutralizing agents such as milk of lime or caustic soda.
- Formation of precipitation products: The target substances react with the precipitants and neutralizing agents and form insoluble hydroxides or other compounds.
Examples:
- Heavy metal precipitation: Heavy metals such as lead, copper, nickel and zinc are precipitated as hydroxides. The reaction equation for the precipitation of copper is:
- Chromium(VI) reduction: Chromium(VI) is reduced with sodium bisulphite to chromium(III) and then precipitated as chromium(III) hydroxide. The reaction equations are:
Flocculation basics
Flocculation often follows precipitation and serves to combine the precipitation products formed into larger agglomerates that can be separated more easily.
Flocculation process
The flocculation process:
- Cationic (positively charged) or anionic (negatively charged) polymers are added to the wastewater. The choice of polymer is decisive for optimum floc formation with very good sedimentation properties.
Aims of flocculation:
- Suspended particles: Removal of suspended solids by forming larger flocs.
- Water clarity: Improves the clarity of the treated water by removing turbidity.
- Wide application: Efficient removal of a wide range of substances, including pre-precipitated heavy metals, emulsified hydrocarbons, fluorides, phosphates, sulphates, dyes and pigments.
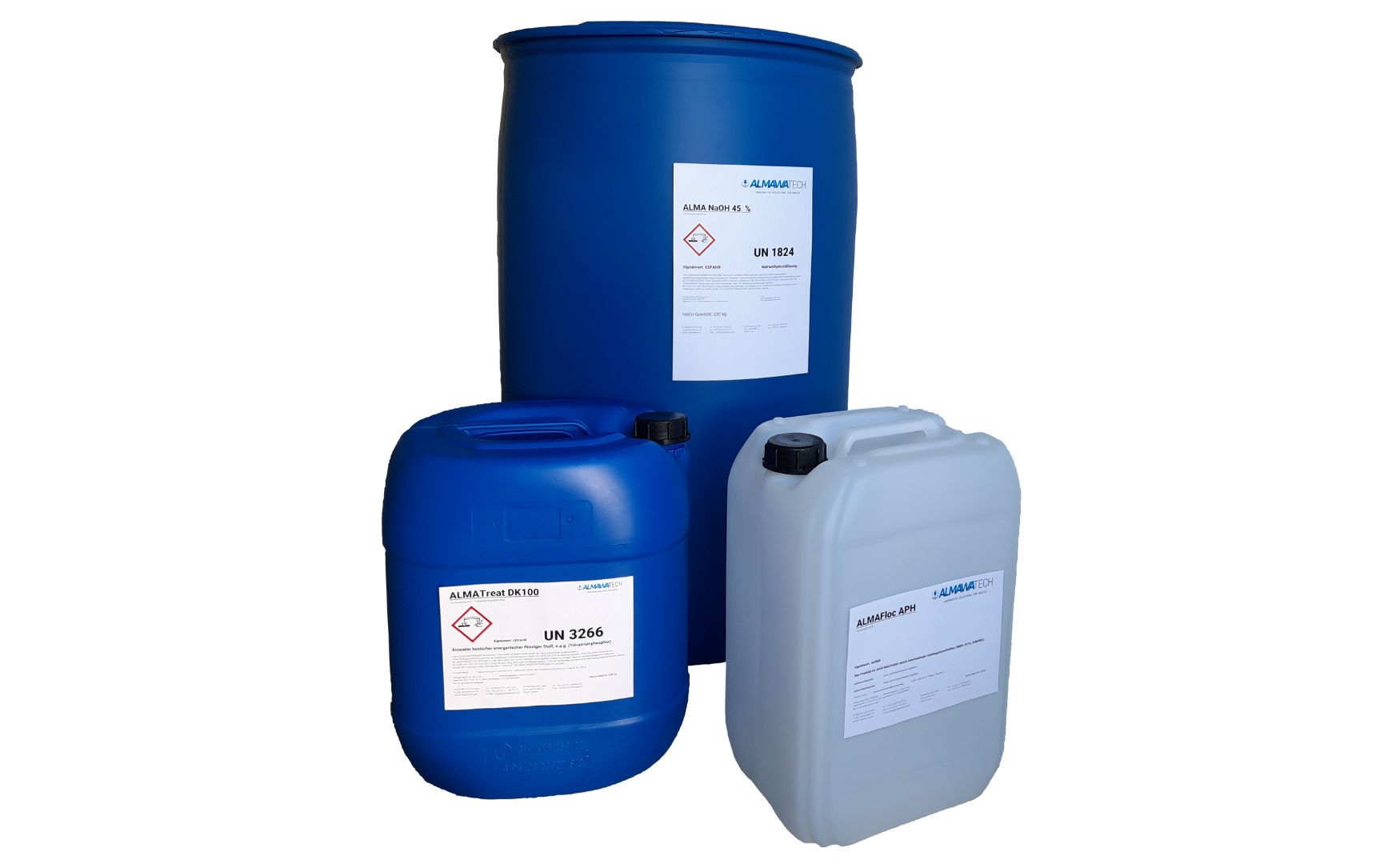

Photo: ALMA Floc APH precipitant and ALMA NaOH neutralizing agent (product series: ALMA AQUA)
Specific applications of chemical-physical wastewater treatment
Cyanide detoxification
Cyanide, a highly toxic anion, is often used in the metalworking industry and must be safely removed before being discharged into the environment. Detoxification is achieved by oxidation, which converts cyanide into less toxic compounds. Typical oxidizing agents are chlorine bleach or hydrogen peroxide, which oxidize the cyanide to cyanate and finally to carbon dioxide and nitrogen. The reaction equation for the oxidation of cyanide (CN-) with hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) to cyanate (OCN-) is as follows
In a further step, the cyanate can be further oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO₂) and nitrogen (N₂):
Heavy metal precipitation
Heavy metals such as lead, copper, nickel and zinc must be removed from wastewater in order to comply with environmental and health regulations. This is done by precipitation, in which soluble heavy metals are converted into insoluble hydroxides. By adding precipitants such as milk of lime or caustic soda and adjusting the pH value to the optimum range for the respective metal precipitation, the metals can be removed from the water. The resulting sludge is then dewatered mechanically, for example using chamber filter presses.
Chromium (VI) reduction
Chromium(VI), a strong oxidizing agent and carcinogen, is mainly used in electroplating and must be reduced before discharge. The reduction is usually carried out with sodium bisulphite, which reduces chromium(VI) to chromium(III), which is then precipitated as chromium(III) hydroxide. This process requires careful pH control to ensure complete reduction.
Pre-treatment for water recycling plants
For companies that want to recycle their wastewater, additional treatment steps are required. Activated carbon filters remove organic compounds and residues that cannot be removed by chemical precipitation. Ion exchangers remove remaining dissolved ions, and reverse osmosis systems provide final purification by filtering out dissolved solids and organic contaminants. These methods combine physical and chemical processes to produce high purity water for reuse in the production process.
Conclusion & summary
The chemical-physical treatment of industrial wastewater is a complex process that combines various technologies and methods to meet legal requirements and protect the environment. Processes such as cyanide detoxification, heavy metal precipitation, chromium (VI) reduction and pre-treatment for water recycling are crucial for effective wastewater treatment. Through pretreatment and the use of advanced technologies, facilities can efficiently treat their wastewater while implementing sustainable practices.
For further information and individual advice on wastewater treatment, please do not hesitate to contact us. You can find out more about our ALMA CHEM MCW CP system at the following link.
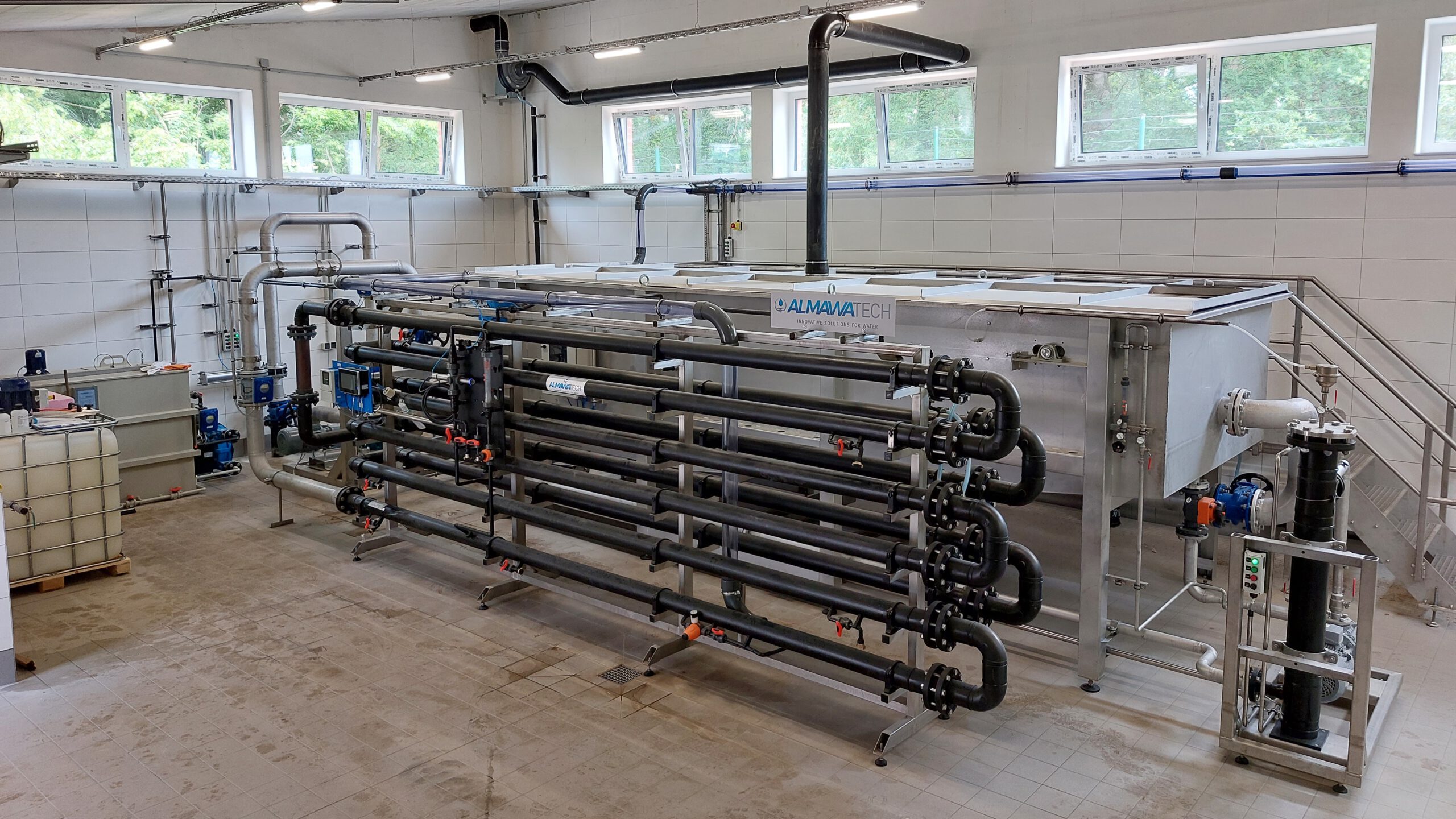

Photo: Flotation plants are also based on the chemical-physical treatment process (plant: ALMA NeoDAF)
If you would like to learn more about the process principles of flotation, please read our blog article "Flotation systems in industrial wastewater treatment: Process basics and areas of application".